WiFi 5 vs. WiFi 6: What's the Difference?
Home and business owners looking for networking gear face an array of choices. WiFi 5 and WiFi 6 products are the two options most people hesitate between.
A glance at product promotions or tech news may immediately tell you that WiFi 5 and WiFi 6 identify different generations of WiFi, with WiFi 6 being newer with better performance.
However, a newer standard does not always mean that it is the one you need. If you're thinking about grabbing the latest generation, you may want to take some time to consider your options beforehand.
To make a rational choice, we first need to understand the key differences between WiFi 5 and WiFi 6.
What are WiFi 5 and WiFi 6?
WiFi 5 (802.11ac WiFi) and WiFi 6 (802.11ax) are parts of the WiFi networking family. The WiFi Alliance simplified naming with labeling based on the generation of WiFi instead of their standards.
WiFi 5, the 5th generation of WiFi, rolled out with Wave 1 certification in mid-2013.
WiFi 6, the 6th generation of WiFi, was introduced in 2018 and hit the market in 2019, featuring OFDMA, 1024-QAM, MU-MIMO (both uplink and downlink), Target Wake Time, and BSS coloring. WiFi 6 is designed to improve speeds, increase efficiency, and reduce congestion in heavy bandwidth usage scenarios by building upon WiFi 5.

What are their differences?
The newest generation of WiFi standards is backward compatible with the previous standards. It represents a significant jump in the technology used and available features. WiFi 6 supports all features of WiFi 5 while bringing more benefits.
- Faster speeds
Each generation of WiFi increases WiFi speeds. So does WiFi 6, though this is not its primary goal. The nominal data rates are raised up to 9.6 Gbps, around 40% higher than that of WiFi 5.
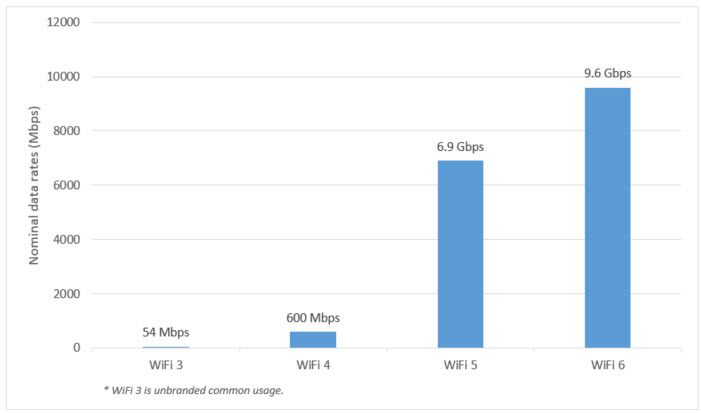
- Higher efficiency
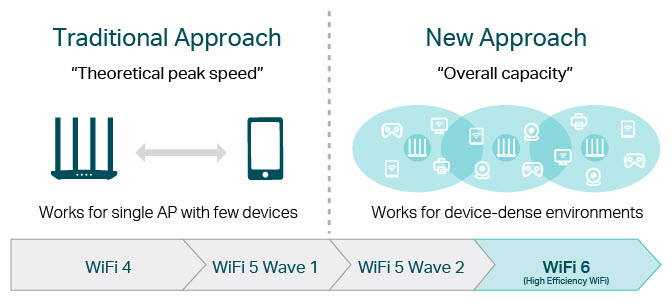
Performance in crowded networks is ultimately WiFi 6's signature feature. Also known as "High-Efficiency WiFi," WiFi 6 shines brightest in device-dense environments like corporate offices, shopping malls, and dense residential apartments. While the nominal data rate improvement against WiFi 5 is around 40%, the overall throughput improvement over an entire network is 300% (hence High Efficiency). This also translates to 75% lower latency. WiFi 6 also maintains steady top speeds while connected to many devices simultaneously, even where previous WiFi versions would stumble.
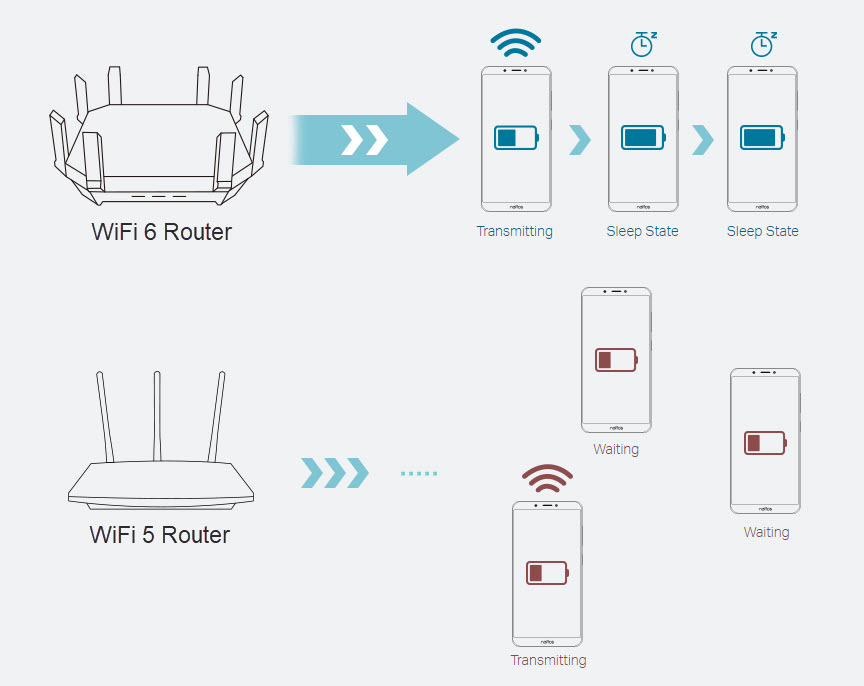
- Improved battery life
Target Wake Time (TWT) allows devices to negotiate when and how often they wake up to send or receive data. This feature increases device sleep time and substantially improves battery life for mobile and IoT devices.
Worldwide adoption of WiFi 5 and WiFi 6 devices
WiFi 6 is seeing broad adoption in WLAN markets around the world.
According to IDC's Worldwide Quarterly Wireless LAN Tracker in Q3 2021:
In the enterprise WLAN market, WiFi 6 APs (access points) made up 62.2% of the revenues in the Dependent AP segment. They accounted for 50.7% of unit shipments within the segment in Q3 2021. WiFi 5 products made up the vast balance of remaining Dependent AP sales.
In the consumer WLAN market, WiFi 6 products continued to grow, rising to make up 27.9% of the consumer segment's total revenue, up from 24.5% in Q2 2021. WiFi 5 APs still account for most revenues (61.4%) and unit shipments (63.6%).
Many products, including smartphones, tablets, PCs, networking products, and some premium-tier home entertainment devices, now feature WiFi 6. The number of products continues to grow. Now, it's time to hunt for a WiFi 6 router to benefit the most from your new WiFi 6 clients!
Reference:
Meet the 6th generation of WiFi
