Frequently asked questions regarding Jumbo Frame (MTU) about TP-Link switches
The popularity of jumbo frame
When talking about Maximum Frame Size or MTU (Maximum Transmission Unit), we mean the maximum frame size that this switch can store and forward.
IEEE 802.3 Ethernet Version 2 defined the maximum frame size, which is 1518 Bytes.
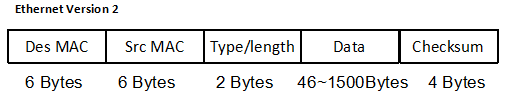
For 802.1Q frame, which added 4 Bytes Tag in the standard Ethernet frame’s Header, then the maximum frame size can be as long as 1522 Byte, we call it “Baby Jumbo Frame”. 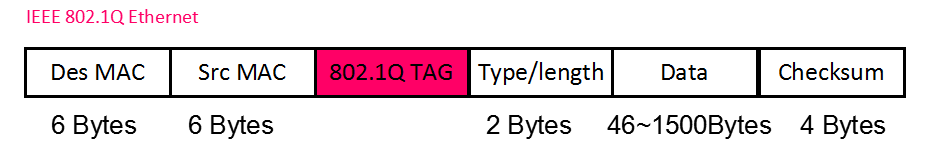
Frame with Data payload bigger than 1500 Bytes is called a “Jumbo Frame”.
The benefit of using Jumbo Frame (often used in data center) is to improve the efficiency of data transferring, since the main cost when a switch store and forward an Ethernet frame is handling the “head” of the frame. For a certain amount of data to be transmitted, the bigger size “Data” part has, the less number of frames will be used to “carry” the data, save the CPU calculating cost of switch.
Make a metaphor, it is just like we order trucks instead of buggies to carry certain amount of goods, one buggy cannot carry as much goods as one truck can, more buggies means more drivers to be payed, more toll need on the way to destination. So it is wiser to carry goods using trucks.
Supportive of Jumbo Frame
Routers, switches, NIC must all Support jumbo frame In order to get the network transmit jumbo frames, any device not supporting jumbo frame, or supported jumbo frame size less than the frame to be transmitted will be fragmented or abandoned.
To know how to generate and test jumbo frame, please click on the link FAQ 697.
Here are some frequently asked questions regarding Jumbo Frame and
TP-Link switches.
1.How can I know if a TP-Link switch supports Jumbo Frame and what is the maximum frame size supported?
Jumbo Frame parameter of TP-Link switches can be found in the product specification on our official website. Take the example of unmanaged switch TL-SG1024, we can go to product specification for TL-SG1024, in “performance” column, we can see that it supports Jumbo Frame with maximum 10K Bytes in frame size.
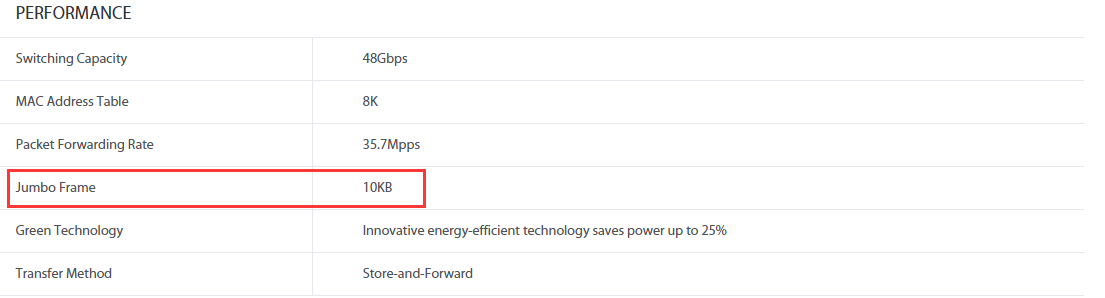
If there is no declaration for Jumbo Frame in product specification for one switch, that means this model number does not support jumbo frame feature, that is to say, the maximum frame size of this switch is 1522 Bytes/Supporting Baby Jumbo frame.
2.How can I enable Jumbo Frame feature on TP-Link switches?
There is no configurations need to be done before you want the switch to forward Jumbo Frame, which means that any TP-Link switch supporting Jumbo Frame will forward Jumbo frame within the allowed maximum size.
3.What can I do if I want to disable jumbo frame feature of TP-Link switches?
There is no CLI that you can use to shut down the Jumbo Frame feature of TP-Link switches.
4.Will Unmanaged Switches forward Tagged Frames/Baby Jumbo Frame?
Yes, VLAN Tagged or Priority Tagged frames, which is also called Baby Jumbo Frame, will be forwarded by Unmanaged Switches transparently, which means that unmanaged switch will not check the Tag information of Baby Jumbo Frame.
5.How to increase or decrease the MTU size of data frame to be transmitted?
Data is made into frames by Network Interface Card, it all depends on the application program on the sender to determine how big size the frame is to be formed on the Network Interface Card. Switch cannot modify the MTU size of the Jumbo Frame.
6.What will happen if the size of jumbo frame to be transmitted exceeds the MTU of a switch?
Fragmentation will be done on NIC or Routers. Data of the Original Jumbo Frame will be divided into smaller fragments and reform a “smaller Frame” according to the minimum MTU of the link allowed in order to pass through the switch. Switch does nothing in the process, it is the sender or routers who fragmented Original Jumbo Frame.
¿Es útil esta pregunta frecuente?
Sus comentarios nos ayudan a mejorar este sitio.







