Archer A6 V2 User Guide
- About This Guide
- Chapter 1 Get to Know About Your Router
- Chapter 2 Connect the Hardware
- Chapter 3 Log In to Your Router
- Chapter 4 Set Up Internet Connection
- Chapter 5 TP-Link Cloud Service
- Chapter 6 Guest Network
- Chapter 7 Parental Controls
- Chapter 8 QoS
- Chapter 9 Network Security
- Chapter 10 NAT Forwarding
- Chapter 11 VPN Server
- Chapter 12 Customize Your Network Settings
-
Chapter 13 Manage the Router
- Set Up System Time
- Control LEDs
- Test the Network Connectivity
- Upgrade the Firmware
- Backup and Restore Configuration Settings
- Set the Router to Reboot Regularly
- Change the Login Password
- Password Recovery
- Local Management
- Remote Management
- System Log
- Monitor the Internet Traffic Statistics
- Configure the System Parameters
- FAQ
- Authentication
Chapter 13 Manage the Router
This chapter will show you the configuration for managing and maintaining your router.
It contains the following sections:
•Test the Network Connectivity
•Backup and Restore Configuration Settings
System time is the time displayed while the router is running. The system time you configure here will be used for other time-based functions like Parental Controls. You can choose the way to obtain the system time as needed.
1.Visit http://tplinkwifi.net, and log in with the password you set for the router.
2.Go to Advanced > System Tools > Time Settings. It is 12-hour time by default, and you can toggle on to change to 24-hour time.
•To get time from the internet:
1.In the Set Time field, select Get automatically from the Internet.

2.Select your local Time Zone from the drop-down list.
3.In the NTP Server I fileld, enter the IP address or domain name of your desired NTP Server.
4.(Optional) In the NTP Server II fileld, enter the IP address or domain name of the second NTP Server.
5.Click Obtain to get the current Internet time and click Save.
•To manually set the date and time:
1.In the Set Time field, select Manually.

2.Set the current Date (In MM/DD/YYYY format).
3.Set the current Time (In HH/MM/SS format).
4.Click Save.
•To set up Daylight Saving Time:
1.Select Enable Daylight Saving Time.

2.Select the correct Start date and time when daylight saving time starts at your local time zone.
3.Select the correct End date and time when daylight saving time ends at your local time zone.
4.Click Save.
The router‘s LEDs indicate router’s activities and status. You can turn on or turn off the LEDs either from the web management page or by pressing the LED button.
1.Visit http://tplinkwifi.net, and log in with the password you set for the router.
2.Go to Advanced > System Tools > LED Control.
3.Toggle to turn on / off the LED.
4.You can enable Night Mode if needed, and set a time period, and then the LEDs will be off during this period.

5.Click Save.
3. Test the Network Connectivity
Diagnostics is used to test the connectivity between the router and the host or other network devices.
1.Visit http://tplinkwifi.net, and log in with the password you set for the router.
2.Go to Advanced > System Tools > Diagnostics.

3.Enter the information with the help of page tips:
1 )Choose Ping or Traceroute as the diagnostic tool to test the connectivity;
•Ping is used to test the connectivity between the router and the tested host, and measure the round-trip time.
•Traceroute is used to display the route (path) your router has passed to reach the tested host, and measure transit delays of packets across an Internet Protocol network.
2 )Enter the IP Address or Domain Name of the tested host.
4.Click Start to begin the diagnostics.
Tips:
Click Advanced, you can modify the ping count or ping packet size. It’s recommended to keep the default value.
The figure below indicates the proper connection between the router and the Yahoo server (www.Yahoo.com) tested through Ping.

The figure below indicates the proper connection between the router and the Yahoo server (www.Yahoo.com) tested through Traceroute.

TP-Link aims at providing better network experience for users.
We will inform you through the web management page if there’s any update firmware available for your router. Also, the latest firmware will be released at the TP-Link official website www.tp-link.com, and you can download it from the Support page for free.
Note:
•Backup your router configuration before firmware upgrade.
•Do NOT turn off the router during the firmware upgrade.
1.Download the latest firmware file for the router from www.tp-link.com.
2.Visit http://tplinkwifi.net, and log in with the password you set for the router.
3.Go to Advanced > System Tools > Firmware Upgrade.
4.Focus on the Device Information section. Make sure the downloaded firmware file is matched with the Hardware Version.
5.Focus on the Manual Upgrade section. Click Browse to locate the downloaded new firmware file, and click Upgrade.
6.Wait a few minutes for the upgrade and reboot to complete.
5. Backup and Restore Configuration Settings
The configuration settings are stored as a configuration file in the router. You can backup the configuration file to your computer for future use and restore the router to a previous settings from the backup file when needed. Moreover, if necessary you can erase the current settings and reset the router to the default factory settings.
1.Visit http://tplinkwifi.net, and log in with the password you set for the router.
2.Go to Advanced > System Tools > Backup & Restore.
•To backup configuration settings:
Click Backup to save a copy of the current settings to your local computer. A ‘.bin’ file of the current settings will be stored to your computer.
•To restore configuration settings from backup:
1.Click Browse to locate the backup configuration file stored on your computer, and click Restore.

2.Wait a few minutes for the restoring and rebooting.
Note: During the restoring process, do not turn off or reset the router.
•To reset the router except your login password and bound TP-Link ID:
1.Click Restore under the Factory Default Restore session.

2.Wait a few minutes for the resetting and rebooting.
Note:
•During the resetting process, do not turn off the router.
•After reset, you can still use the current login password or the TP-Link ID to log in to the web management page.
•To reset the router to factory default settings:
1.Click Factory Restore under the Factory Default Restore session.

2.Wait a few minutes for the resetting and rebooting.
Note:
•During the resetting process, do not turn off or reset the router.
•We strongly recommend you backup the current configuration settings before resetting the router.
6. Set the Router to Reboot Regularly
The Scheduled Reboot feature cleans the cache to enhance the running performance of the router.
1.Visit http://tplinkwifi.net, and log in with the password you set for the router.
2.Go to Advanced > System Tools > Reboot Schedule.
3.Check the box to enable Reboot Schedule.

4.Specify the Reboot Time when the router reboots and Repeat to decide how often it reboots.
5.Click Save.
The account management feature allows you to change your login password of the web management page.
1.Visit http://tplinkwifi.net, and log in with the password you set for the router.
2.Go to Advanced > System Tools > Administration and focus on the Account Management section.

3.Enter the old password, then a new password twice (both case-sensitive). Click Save.
4.Use the new password for future logins.
This feature allows you to recover the login password you set for you router in case you forget it.
1.Visit http://tplinkwifi.net, and log in with the password you set for the router.
2.Go to Advanced > System Tools > Administration and focus on the Password Recovery section.
3.Tick the Enable Password Recovery checkbox.
4.Specify a mailbox (From) for sending the recovery letter and enter its SMTP Server address. Specify a mailbox (To) for receiving the recovery letter. If the mailbox (From) to send the recovery letter requires encryption, select Enable Authentication and enter its username and password.
Tips:
•SMTP server is available for users in most webmail systems. For example, the SMTP server address of Gmail is smtp.gmail.com. You can refer to their Help page to learn the SMTP server address.
•Generally, Enable Authentication should be selected if the login of the mailbox requires username and password.

5.Click Save.
You can click Test Email to test whether the configuration is successful.
To recover the login password, please visit http://tplinkwifi.net, click Forgot Password? on the login page and follow the instructions to set a new password.
This feature allows you to limit the number of client devices on your LAN from accessing the router by using the MAC address-based authentication.
1.Visit http://tplinkwifi.net, and log in with the password you set for the router.
2.Go to Advanced > System Tools > Administration and complete the settings in Local Management section as needed.
•Enable Local Management via HTTPS
Toggle on Local Management via HTTPS if you want to access the router via HTTPS and HTTP, or keep it disabled if you only want to access the router via HTTP.

•Allow all LAN connected devices to manage the router:
Toggle on Access for All LAN Connected Devices.

•Allow specific devices to manage the router:
1.Toggle off Access for All LAN Connected Devices.
2.Click Add.

3.Click View Existing Devices and select the device to manage the router from the Existing Devices list, or enter the MAC address of the device manually.
4.Specify a Description for this entry.
5.Tick the Enable This Entry checkbox.
6.Click OK.
This feature allows you to control remote devices’ authority to manage the router.
1.Visit http://tplinkwifi.net, and log in with the password you set for the router.
2.Go to Advanced > System Tools > Administration and complete the settings in Remote Management section as needed.
3.Select the checkbox to enable Remote Management function.
4.Keep the HTTPs Port and HTTP Port as the default settings.
5.Select to decide which remote device can access the router remotely. Choose All Devices to allow all remote devices to manage the router; select Specified Device and enter the IP address of a remote device to allow only this device to manage the router.
6.Click Save.
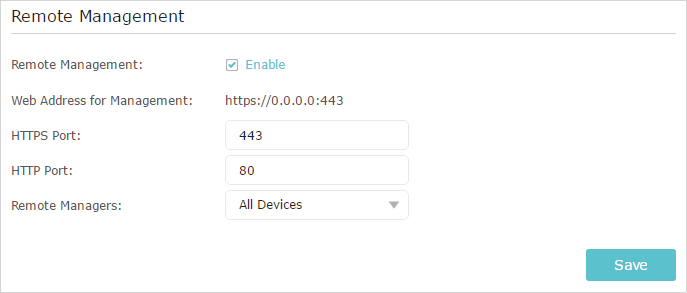
Devices on the internet can access manage the router via the Web Address for Management, such as https://0.0.0.0:43 shown.
When the router does not work normally, you can save the system log and send it to the technical support for troubleshooting.
•To save the system log in local:
1.Visit http://tplinkwifi.net, and log in the password you set for the router.
2.Go to Advanced > System Tools > System Log.
3.Choose the type and level of the system logs as needed.
4.Click Save Log to save the system logs to local.

•To send the system log to a mailbox at a fixed time:
For example, I want to check my router’s working status at a fixed time every day, however, it’s too troublesome to log in to the web management page every time I want to go checking. It would be great if the system logs could be sent to my mailbox at 8 a.m. every day.
1.Visit http://tplinkwifi.net, and log in with the password you set for the router.
2.Go to Advanced > System Tools > System Log.
3.Click Mail Settings.
4.Enter the information required:

1 )From: Enter the email address used for sending the system log.
2 )To: Enter the recipient’s email address, which can be the same as or different from the sender’s email address.
3 )SMTP Server: Enter the SMTP server address.
Tips: SMTP server is available for users in most webmail systems. For example, the SMTP server address of Hotmail is smtp-mail.outlook.com. You can refer to their Help page to learn the SMTP server address.
4 )Select Enable Authentication.
Tips: Generally, Enable Authentication should be selected if the login of the mailbox requires username and password.
5 )Username: Enter the email address used for sending the system log.
6 )Password: Enter the password to login the sender’s email address.
7 )Select Enable Auto Mail.
Tips: The router will send the system log to the designated email address if this option is enabled.
8 )Set a fixed time. The recipient will receive the system log sent at this time every day.
5.Click Save.
12. Monitor the Internet Traffic Statistics
The Traffic Statistics page displays the network traffic of the LAN, WAN and WLAN sent and received packets, allowing you to monitor the volume of Internet traffic statistics.
1.Visit http://tplinkwifi.net, and log in with the password you set for the router.
2.Go to Advanced > System Tools > Traffic Statistics.
3.Toggle on Traffic Statistics, and then you can monitor the traffic statistics in Traffic Statistics List section.

Click Refresh to update the statistic information on the page.
Click Reset All to reset all statistic values in the list to zero.
Click Delete All to delete all statistic information in the list.
Click to reset the statistic information of the specific device.
Click to delete the specific device item in the list.
13. Configure the System Parameters
13.1. Wireless Advanced
1.Visit http://tplinkwifi.net, and log in with the password you set for the router.
2.Go to Advanced > System Tools > System Parameters.
3.Configure the advanced settings of your wireless network and click Save.
Note:
If you are not familiar with the setting items on this page, it’s strongly recommended to keep the provided default values; otherwise it may result in lower wireless network performance.

•Beacon Interval - Enter a value between 40-1000 milliseconds for Beacon Interval here. Beacon Interval value determines the time interval of the beacons. The beacons are the packets sent by the router to synchronize a wireless network. The default value is 100.
•RTS Threshold - Here you can specify the RTS (Request to Send) Threshold. If the packet is larger than the specified RTS Threshold size, the router will send RTS frames to a particular receiving station and negotiate the sending of a data frame. The default value is 2346.
•DTIM Interval - This value determines the interval of the Delivery Traffic Indication Message (DTIM). A DTIM field is a countdown field informing clients of the next window for listening to broadcast and multicast messages. When the router has buffered broadcast or multicast messages for associated clients, it sends the next DTIM with a DTIM Interval value. You can specify the value between 1-15 Beacon Intervals. The default value is 1, which indicates the DTIM Interval is the same as Beacon Interval.
•Group Key Update Period - Enter the number of seconds (minimum 30) to control the time interval for the encryption key automatic renewal. The default is 0, indicating no key renewal.
•Enable WMM - WMM function can guarantee the packets with high-priority messages being transmitted preferentially. It is strongly recommended to enable this function.
•Enable Short GI - It is recommended to enable this function, for it will increase the data capacity by reducing the guard interval time.
•AP Isolation Feature - If you want to confine and restrict all devices connected to your network from internet interacting with each other but still able to access the internet, select the checkbox to enable this function.
13.2. WDS
For example, my house covers a large area. The wireless coverage of the router I’m using (the root router) is limited. I want to use an extended router to extend the wireless network of the root router.
Note:
•WDS bridging only requires configuration on the extended router.
•WDS bridging function can be enabled either in 2.4GHz frequency or 5GHz frequency for a dual-band router. We use the WDS bridging function in 2.4GHz frequency as example.
1.Visit http://tplinkwifi.net, and log in with the password you set for the router.
2.Configure the IP address of the router:
1 )Go to Advanced > Network > LAN, configure the IP address of the extended router to be in the same subnet with the root router; (For example, the IP address of the root router is 192.168.0.1, the IP address of the extended router can be 192.168.0.2~192.168.0.254. We take 192.168.0.2 as example.)
2 )Click Save.
Note: Log in to the web management page again if the IP address of the router is altered.

3.Survey the SSID to be bridged:
1 )Go to Advanced > System Tools > System Parameters, focus on the 2.4GHz WDS section and click Enable WDS Bridging.
2 )Click Survey, locate the root router’s SSID and click Choose (Here we take
TP-Link_4F98 as example).
3 )If the root router has wireless password, you should enter the wireless password of the root router.
4 )Click Save.

4.Disable DHCP:
1 )Go to Network > DHCP Server.
2 )Deselect Enable DHCP Server and click Save.
Now you can go to Advanced > Status > Wireless to check the WDS status. When the WDS status is Run, it means WDS bridging is successfully built.
13.3. WPS
Enable this function to easily set up and connect your WPS-enabled devices to your Wi-Fi at a push of the WPS button.
13.4. NAT
Select the checkbox to Enable/Disable the NAT (Network Address Translation) and NAT Boost function. The router’s NAT feature makes devices on the LAN use the same public IP address to communicate with devices on the internet, which protects the local network by hiding IP addresses of the devices.

13.5. DoS Protection
DoS Protection can protect your home network against DoS attacks from flooding your network with server requests. Follow the steps below to configure DoS Protection.
1.Visit http://tplinkwifi.net, and log in with the password you set for the router.
2.Go to Advanced > System Tools > System Parameters.

3.Configure ICMP-FLOOD Attack Filtering, UDP-FlOOD Attack Filtering and TCP-SYN-FLOOD Attack Filtering.
•ICMP-FLOOD Attack Filtering - Enter a value between 5 and 7200 ICMP packets to trigger the ICMP-FLOOD protection immediately when the number of packets exceeds the preset threshold value.
•UDP-FlOOD Attack Filtering -Enter a value between 5 and 7200 UDP packets to trigger the UDP-FLOOD protection immediately when the number of packets exceeds the preset threshold value.
•TCP-SYN-FLOOD Attack Filtering - Enter a value between 5 and 7200 TCP-SYN packets to trigger the TCP-SYN-FLOOD protection immediately when the number of packets exceeds the preset threshold value.
4.Click Save.
13.6. Duplex
Select the duplex type from the drop-down list and click Save. Duplex (or full-duplex) communication can go in both directions at once, while half-duplex communication can go only one way at a time. If you are not sure, you can keep the default Auto Negotiation.